What Does Ringworm Look Like on a Dog: Spot the Signs!

Ringworm on a dog looks like dandruff-like scaling, red lesions, skin scaling, and circular patches of hair loss. It can resemble bacterial infections or allergies.
Ringworm is treated with topical and systemic therapy, eliminating all environmental contamination for successful treatment. Ringworm is contagious to humans through direct contact with an infected dog, especially if the skin is broken or compromised. Understanding the appearance and treatment of ringworm in dogs is crucial for prompt intervention and preventing its spread to other pets or family members.
Let’s delve deeper into the signs, symptoms, and management of ringworm in dogs to ensure the well-being of our furry companions.
Credit: blog.tryfi.com
Identifying Ringworm In Dogs
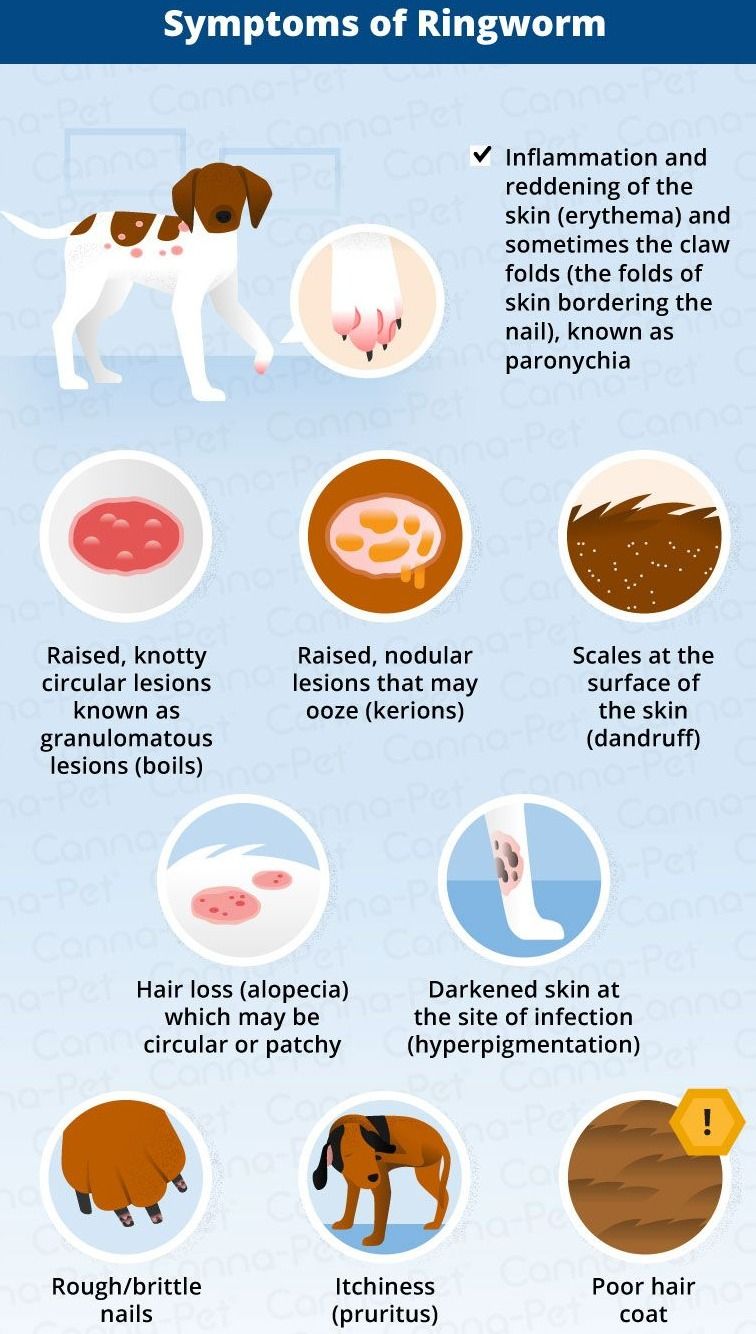
Identifying ringworm in dogs involves looking for circular areas of hair loss, itchiness, dandruff, darkened skin, scabs, inflamed skin, and broken hairs. These signs may indicate ringworm infection, which appears as red lesions, scaling, and circular patches of hair loss on a dog’s body.
Common Signs And Symptoms
Ringworm is a fungal infection that commonly affects dogs. It is highly contagious and can spread quickly from one pet to another. If your dog has ringworm, you might notice the following signs and symptoms:- Circular areas of hair loss
- Itchiness
- Rash
- Dandruff-like scaling in the depths of the coat
- Red lesions on the head, chest, forelegs, and the ridge of the back
- Scaling, crusting, thickening, and reddening of the skin
- Darkened skin
- Scabs or lesions on the skin
- Inflamed areas of skin
- Brittle or broken hairs
- Hair loss
Visual Characteristics Of Ringworm
To identify ringworm in dogs, it is important to understand its visual characteristics. Ringworm characteristically appears in a circular or ring-shaped pattern on the skin, usually causing the skin to turn red, lose hair, and swell. The circular patches of hair loss are often accompanied by scaly, crusty, or thickened skin. The lesions may also be itchy or painful for your furry friend. If you suspect your dog has ringworm, it is important to consult a veterinarian immediately. They can perform a skin culture or other diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment plan. Remember, early detection and treatment of ringworm can help prevent its spread to other pets and humans in your household.Misdiagnosis: Conditions Similar To Ringworm
When identifying ringworm on a dog, it’s essential to be aware of conditions that may resemble it, such as bacterial skin infections, skin yeast infections, and allergies. Ringworm typically presents as circular patches of hair loss, dandruff-like scaling, and red lesions on the skin.
It’s important to consult a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Bacterial Infections That Mimic Ringworm
Misdiagnosing ringworm in dogs can occur due to similar-looking conditions such as bacterial skin infections, also known as pyoderma. These infections can manifest with redness, itching, and hair loss—symptoms that overlap with ringworm. However, bacterial infections typically do not have the distinct circular pattern seen in ringworm lesions.Allergies And Their Differentiating Factors
Allergies in dogs can be mistaken for ringworm due to itching, redness, and skin lesions. However, allergies often present with additional symptoms such as sneezing, watery eyes, and ear infections. Unlike ringworm, allergies do not exhibit the classic circular patches of hair loss. In summary, bacterial infections and allergies are common conditions that can be misdiagnosed as ringworm in dogs. It is crucial for pet owners to seek veterinary evaluation for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.Initial Indicators Of Ringworm
When it comes to identifying ringworm on your dog, it’s crucial to recognize the initial indicators to seek prompt treatment and prevent the spread of the infection. Knowing the early physical changes and behavioral clues pointing to discomfort can help you take swift action to address the issue. Let’s delve into these crucial signs of ringworm in dogs.
Early Physical Changes
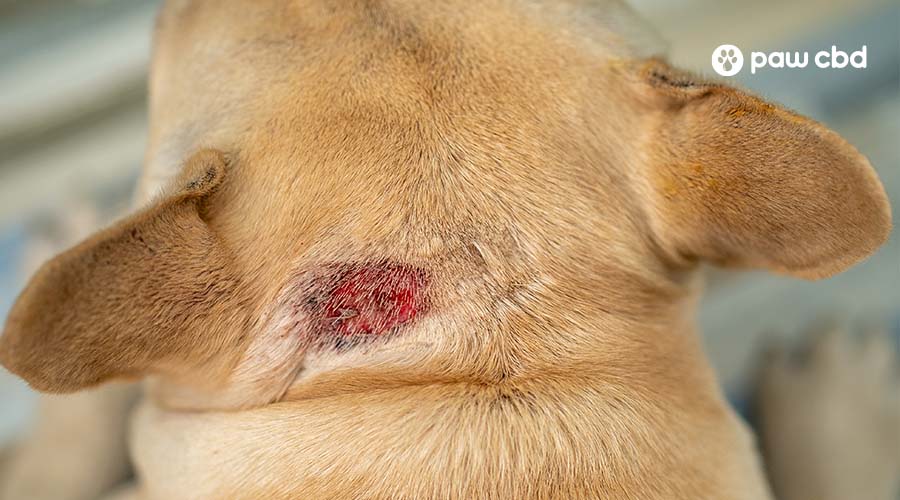
Ringworm on a dog can initially appear as circular areas of hair loss, itch, rash, dandruff, darkened skin, scabs or lesions on the skin, inflamed areas of skin, brittle or broken hairs, and overall hair loss. These physical changes may manifest in various parts of the dog’s body, including the head, chest, forelegs, and the ridge of the back.
Behavioral Clues Pointing To Discomfort
Dogs with ringworm may exhibit behavioral changes indicative of discomfort, such as excessive scratching, licking, or chewing at the affected areas. They may also show signs of irritability, restlessness, or reluctance to be touched in specific areas of their body. Observing these behavioral clues can provide valuable insights into the dog’s discomfort related to ringworm.
Credit: www.pawcbd.com
Examining The Affected Skin
When examining a dog for ringworm, it’s essential to closely observe the affected skin. Ringworm typically manifests in specific ways, and recognizing these visual cues can aid in prompt identification and treatment.
Texture And Appearance
The affected skin may exhibit changes in texture, often becoming rough or scaly to the touch. Additionally, ringworm can cause the skin to appear inflamed and irritated, sometimes leading to the formation of scabs or lesions.
Color Variations And Patterns
Ringworm can present with various color variations and patterns on the skin. The affected areas may display redness, darkening of the skin, or the formation of circular patches of hair loss, also known as alopecia.
Hair Loss Patterns
Ringworm on a dog appears as circular hair loss patches, inflamed skin, scabs, and dandruff-like scaling. It may cause red lesions on the head and forelegs, leading to brittle or broken hairs. Treatment involves topical and systemic therapy to eliminate the fungal infection.
Typical Areas Of Alopecia
Ringworm on a dog often manifests as circular patches of hair loss, also known as alopecia. These patches may appear on the head, tail, or the ridge of the dog’s back. Hair loss caused by ringworm can also occur on the chest, forelegs, and other parts of the body. The circular areas of alopecia can vary in size and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as dandruff-like scaling and red lesions.
Understanding Hair Breakage In Ringworm
When a dog is affected by ringworm, the hair loss is not solely due to the fungus itself. The infection weakens the hair shaft, making it prone to breakage. This leads to brittle or broken hairs in the affected areas. Understanding this aspect is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of ringworm in dogs.

Credit: companionpetstn.com
Ringworm: Beyond The Skin
Ringworm is a common fungal infection in dogs that can have effects beyond the skin. Understanding the systemic impact and contagious nature of ringworm is essential for responsible pet ownership.
Systemic Effects On A Dog’s Health
Ringworm can have systemic effects on a dog’s health, impacting not only the skin but also the overall well-being of the animal. In severe cases, the fungal infection can lead to hair loss, inflammation, and the formation of scabs or lesions on the skin. It can also cause itching, dandruff, and darkened skin, affecting the dog’s comfort and quality of life.
Contagiousness To Humans And Other Pets
Ringworm is highly contagious and can spread from dogs to humans and other pets. The fungal spores can survive in the environment for an extended period, posing a risk of transmission to anyone in close contact with the infected dog. It’s crucial to take preventive measures and seek prompt treatment to prevent the spread of ringworm to other animals and family members.
Treatment Options For Canine Ringworm
Ringworm is a common fungal infection in dogs that can cause circular patches of hair loss, itching, and skin irritation. Effective treatment is essential to eliminate the infection and prevent it from spreading to other pets or humans.
Topical Therapies
- Antifungal shampoos and creams can be applied directly to the affected areas
- Regular bathing with medicated shampoos helps to reduce fungal spores on the skin
- Topical treatments are often used in combination with oral medications for better results
Oral Medications And Their Effectiveness
- Oral antifungal drugs: such as fluconazole or itraconazole are commonly prescribed
- Systemic therapy: helps to treat the infection from within the body
- Combination therapy: using both oral and topical treatments is often the most effective approach
It’s important to follow your veterinarian’s recommendations for the duration of treatment to ensure complete eradication of the ringworm infection. Regular follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor your dog’s progress and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
Preventing Ringworm In Dogs
Ringworm on a dog appears as circular patches of hair loss, red lesions, scaling, crusting, and thickened skin. Other conditions like bacterial infections or allergies can mimic ringworm symptoms in dogs. Treatment involves topical and systemic therapy to eliminate the infection.
Environmental Decontamination
Ringworm is a highly contagious fungal infection that can easily spread from one dog to another and even to humans. Environmental decontamination is crucial to prevent the spread of ringworm in dogs. It involves cleaning and disinfecting all the surfaces that the infected dog has come into contact with. This includes the dog’s bedding, toys, grooming tools, and any other items that the dog has been in contact with. Use a disinfectant solution to clean these items thoroughly and let them dry completely before use.Tips For Reducing The Risk Of Infection
Prevention is always better than cure, and it is no different when it comes to ringworm in dogs. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of infection:- Regularly bathe and groom your dog to keep their coat clean and healthy.
- Avoid contact with infected dogs or animals.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling an infected dog.
- Do not share grooming tools or other items with an infected dog.
- Keep your dog’s living area clean and well-ventilated.
- Feed your dog a healthy, balanced diet to boost their immune system.
In Conclusion
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that can affect dogs of all ages and breeds. It is important to keep an eye out for the early signs of ringworm and take action immediately if you suspect your dog may be infected. With proper treatment and preventative measures, you can keep your dog healthy and free from ringworm.Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Tell If My Dog Has Ringworm?
Signs of ringworm in dogs include circular patches of hair loss, red lesions, scaling, and crusting of the skin. Other signs may include dandruff-like scaling and inflamed areas.
What Is Mistaken For Ringworm In Dogs?
Bacterial skin infections, skin yeast infections, and allergies are commonly mistaken for ringworm in dogs.
How Do You Treat Ringworm On A Dog?
To treat ringworm on a dog, a combination of topical and systemic therapy is common. This involves using creams, ointments, or shampoos on the affected areas, as well as administering anti-fungal drugs orally. It’s important to eliminate all environmental contamination to ensure successful treatment.
Ringworm on dogs can also be contagious to humans, so caution should be taken.
How Contagious Is Ringworm From Dog To Human?
Ringworm from dogs to humans is contagious through direct contact. Skin-to-skin contact can transmit the infection.
Conclusion
Recognizing ringworm on your dog is crucial for timely treatment. Look for circular hair loss, itchiness, rash, or scabs on the skin. Early detection and appropriate treatment can prevent the spread of ringworm to other pets or humans. Regular check-ups and prompt action are essential for your pet’s well-being.



