How to Become an Anesthesiologist: Your Complete Guide

To become an anesthesiologist, complete a bachelor’s degree, attend medical school, and complete a residency program. Anesthesiologists play a crucial role in ensuring patients’ comfort and safety during surgeries and other medical procedures.
These specialized physicians administer anesthetics, monitor patients’ vital signs, and manage pain before, during, and after procedures. Becoming an anesthesiologist requires a strong educational foundation, dedication, and attention to detail. Pursuing this career path involves rigorous training, continuous learning, and a commitment to providing high-quality patient care.
Anesthesiologists must also obtain licensure and certification to practice in their respective jurisdictions. It is a challenging yet rewarding profession that offers opportunities to make a significant impact in healthcare.
The Role Of An Anesthesiologist
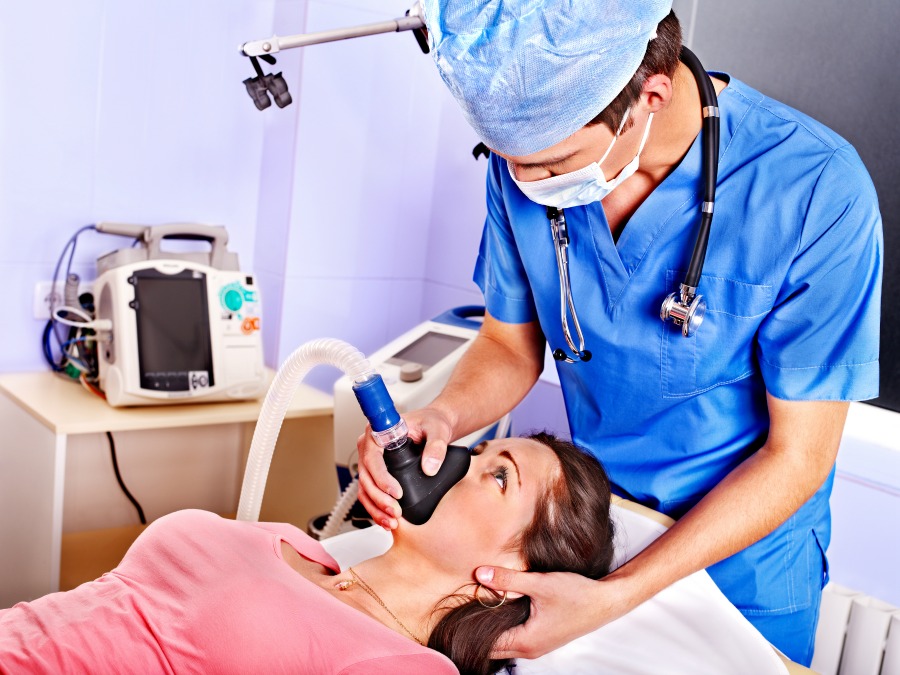
When it comes to the medical field, anesthesiologists play a crucial role in ensuring patient comfort and safety during surgical procedures. Their specialized expertise in administering anesthesia and managing pain makes them integral members of the surgical team. Let’s delve into the key responsibilities and work environment of an anesthesiologist.
Key Responsibilities
- Administering various types of anesthesia to ensure patient comfort during surgical procedures.
- Monitoring and managing vital signs and patient status throughout the surgery.
- Developing and implementing individualized anesthesia plans based on patient needs and medical history.
- Providing post-operative pain management and critical care support.
- Collaborating with surgeons and other medical professionals to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Work Environment
Anesthesiologists typically work in hospitals, surgical centers, and outpatient clinics. They spend a significant amount of time in operating rooms, where they administer anesthesia and closely monitor patients during surgery. The work environment can be fast-paced and demanding, requiring anesthesiologists to remain focused and attentive throughout lengthy procedures.
Credit: www.howtobecome.com
Educational Pathway
Embark on the educational pathway to becoming an anesthesiologist by completing a bachelor’s degree, medical school, and residency training. Gain expertise in administering anesthesia and managing patients’ pain to excel in this critical medical field.
Becoming an anesthesiologist is a long and rigorous journey that requires extensive education and training. The educational pathway to becoming an anesthesiologist is not only challenging but also rewarding. In this blog post, we will explore the educational requirements and curriculum required to become an anesthesiologist.
Undergraduate Requirements
Before you can enroll in medical school, you must first complete a Bachelor’s degree program. The undergraduate program must be completed in a related field, such as biology, chemistry, or pre-med. During your undergraduate program, you should take courses in math, physics, and biology to develop a strong foundation in the sciences. Additionally, participating in extracurricular activities such as volunteering, research, or internships can help strengthen your application to medical school.
Medical School Curriculum
After completing your undergraduate degree, you must then enroll in medical school. Medical school typically takes four years to complete. During your first two years of medical school, you will take courses in the basic sciences, such as anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and medical ethics. During the last two years of medical school, you will gain hands-on experience through clinical rotations in various medical specialties, including anesthesiology. The curriculum for medical school is rigorous and requires a significant amount of study and dedication. Therefore, it is essential to stay organized and develop good study habits to succeed in medical school. After completing medical school, you will then enter a residency training program in anesthesiology. The residency training program typically lasts for four years. During your residency, you will gain hands-on experience in providing anesthesia to patients in various medical settings. You will also take courses and participate in conferences to further develop your knowledge and skills in anesthesiology.
Certification And Continuing Education
After completing your residency program, you must then become board-certified in anesthesiology. The American Board of Anesthesiology (ABA) administers the certification exam for anesthesiologists. Once certified, it is essential to participate in continuing education programs to stay up-to-date with the latest advances and techniques in the field of anesthesiology. In conclusion, becoming an anesthesiologist requires a significant amount of education and training. The journey is challenging, but the rewards are immeasurable. By completing the undergraduate requirements, medical school curriculum, residency training, and certification, you can become a skilled anesthesiologist and make a difference in the lives of your patients.
Medical Licensing
To become an anesthesiologist, obtaining the necessary medical licensing is crucial. The process involves completing the required examinations and fulfilling specific criteria set by the medical board in your country or state. In the United States, this involves the USMLE Steps and State Licensure.
Usmle Steps
The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) is a three-step examination process that assesses a physician’s ability to apply medical knowledge and skills to patient care. These steps are:
- Step 1: This exam focuses on basic science principles and is typically taken after the second year of medical school.
- Step 2: Step 2 is further divided into two components:
- Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK): This exam assesses clinical knowledge and is usually taken during the fourth year of medical school.
- Step 2 Clinical Skills (CS): Step 2 CS evaluates clinical skills and is a practical exam conducted in a clinical setting.
- Step 3: Step 3 is taken after completing the first year of residency and focuses on patient management and decision-making.
State Licensure
Once you have successfully completed the USMLE Steps, you will need to obtain state licensure to practice as an anesthesiologist. Each state has its own specific requirements, but common criteria include:
- Completing an application and paying the required fees
- Providing documentation of your medical education and training
- Passing a criminal background check
- Passing a state-specific licensing examination, if applicable
It is important to thoroughly research and understand the licensing requirements of the state in which you plan to practice. Some states may have additional requirements or variations in the application process.
By successfully completing the USMLE Steps and obtaining state licensure, you will be on your way to becoming a licensed anesthesiologist. These steps ensure that you have the necessary knowledge, skills, and qualifications to provide safe and effective anesthesia care to patients.
Residency Training
Residency training is a crucial step in the journey to becoming an anesthesiologist. This phase involves hands-on experience and advanced medical education, allowing aspiring anesthesiologists to develop the skills and expertise necessary to provide safe and effective anesthesia care to patients.
Choosing A Program
When selecting a residency program, consider the program’s accreditation, reputation, and the types of clinical experiences it offers. Look for programs that align with your career goals and provide a diverse range of cases to enhance your learning.
What To Expect During Residency
During residency, you will undergo rigorous training in various anesthesia subspecialties, including pediatric anesthesia, obstetric anesthesia, critical care medicine, and pain management. Expect to work long hours, participate in on-call rotations, and engage in continuous learning through didactic sessions and hands-on clinical experiences.
Fellowship And Specialization
After completing medical school and residency, the next step for aspiring anesthesiologists is to pursue a fellowship and specialize in a specific area of anesthesiology. This advanced training allows them to gain expertise and knowledge in specialized techniques and procedures. There are several areas of subspecialization within anesthesiology, each offering unique opportunities and challenges.
Advanced Subspecialties
Anesthesiology offers a wide range of advanced subspecialties that anesthesiologists can choose to specialize in. These subspecialties include:
- Pain Medicine: Focusing on the management of acute and chronic pain conditions.
- Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology: Specializing in anesthesia for heart and chest surgeries.
- Pediatric Anesthesiology: Providing anesthesia care to children undergoing surgery or medical procedures.
- Neuroanesthesiology: Focusing on anesthesia for neurosurgical procedures and interventions.
- Obstetric Anesthesiology: Specializing in anesthesia for labor and delivery, ensuring the well-being of both mother and baby.
- Critical Care Medicine: Providing intensive care to patients in critical conditions, often in an ICU setting.
Benefits Of Further Training
Further training through fellowship and specialization offers several benefits to anesthesiologists:
- Expertise: It allows anesthesiologists to develop expertise in a specific area, enhancing their skills and knowledge.
- Career Opportunities: Specializing in a subspecialty can open up various career opportunities, including academic positions, research, and leadership roles.
- Improved Patient Care: With advanced training, anesthesiologists can provide specialized care to patients, ensuring better outcomes and patient satisfaction.
- Professional Growth: Fellowship and specialization provide avenues for professional growth and continuous learning, keeping anesthesiologists updated with the latest advancements in their field.
By pursuing a fellowship and specializing in a subspecialty, anesthesiologists can elevate their careers, contribute to the field of anesthesiology, and provide optimal care to their patients.
Board Certification
Board certification is a crucial step in the journey to becoming an anesthesiologist. It demonstrates a high level of expertise and skill in the field and is an important credential for professional advancement.
The Certification Process
The certification process for anesthesiologists involves completing an accredited anesthesiology residency program after medical school. This is followed by passing the written and oral exams administered by the American Board of Anesthesiology (ABA). These exams assess medical knowledge, patient care, and procedural skills.
Maintaining Certification
After achieving board certification, anesthesiologists must maintain their certification through continuous learning and professional development. This involves participating in lifelong learning and periodic assessments to ensure they stay updated with the latest advancements in the field.
Skills For Success
To become an anesthesiologist, aspiring individuals must acquire a strong foundation in science and math during their education. Developing excellent critical thinking skills and attention to detail is crucial for success in this specialized medical field. Additionally, gaining hands-on experience through internships and residencies is essential for honing the skills needed to excel as an anesthesiologist.
Technical Proficiency
Anesthesiologists must possess strong medical knowledge and proficiency in administering anesthesia.
Soft Skills And Communication
Effective communication and empathy are crucial for anesthesiologists to comfort and reassure patients.

Credit: anest.ufl.edu
Career Opportunities And Outlook
Anesthesiology offers diverse employment settings and promising future trends.
Employment Settings
- Hospitals
- Surgical Centers
- Private Practices
- Academic Institutions
Future Trends In Anesthesiology
- Increased Demand for Pain Management Specialists
- Advancements in Technology
- Collaboration with Other Specialties

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Years Of Education Does It Take To Become An Anesthesiologist?
Becoming an anesthesiologist requires completing a bachelor’s degree, medical school, and a residency program. This process typically takes around 12 years of education and training.
What Skills Are Required To Become An Anesthesiologist?
Anesthesiologists need to have strong communication skills, attention to detail, critical thinking abilities, and the ability to remain calm under pressure. They also need to have a thorough understanding of human anatomy, pharmacology, and physiology.
What Types Of Procedures Do Anesthesiologists Perform?
Anesthesiologists are responsible for administering and monitoring anesthesia during surgeries and other medical procedures. They also manage patients’ pain levels before, during, and after procedures, and may be involved in critical care medicine.
How Much Does An Anesthesiologist Make Per Year?
Anesthesiologists are among the highest-paid medical professionals, with an average annual salary of around $300,000 in the United States. Salary can vary depending on location, experience, and other factors.
Conclusion
Becoming an anesthesiologist requires dedication, perseverance, and years of rigorous education and training. By following the necessary steps, such as completing a bachelor’s degree, attending medical school, and undergoing a residency program, individuals can embark on a rewarding career in this specialized field of medicine.
With a strong focus on patient safety and comfort, anesthesiologists play a crucial role in surgical procedures, ensuring that patients receive the appropriate anesthesia and pain management. Aspiring anesthesiologists should also stay updated on the latest advancements and technologies in the field to provide the best possible care to their patients.
By pursuing this path, one can contribute to the medical community and make a lasting impact on the lives of others.



