How Long Does Meth Stay in Your System? Quick Facts

Methamphetamine can stay in your system for up to three days after use. It can be detected in urine, blood, and saliva tests.
Meth can stay in hair follicles for up to 90 days. The length of time meth stays in your system can vary depending on factors such as the amount used, frequency of use, and individual metabolism. Methamphetamine, commonly referred to as meth, is a highly addictive stimulant drug that affects the central nervous system.
It is a synthetic substance that can be smoked, snorted, injected, or taken orally. Meth creates a feeling of euphoria, increased energy, and heightened alertness. However, it also has many negative side effects, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, paranoia, and aggression. Meth use can lead to addiction, physical and mental health problems, and even death. In this blog post, we will discuss how long meth stays in your system and the factors that can affect detection time.
Introduction To Meth Detection Times
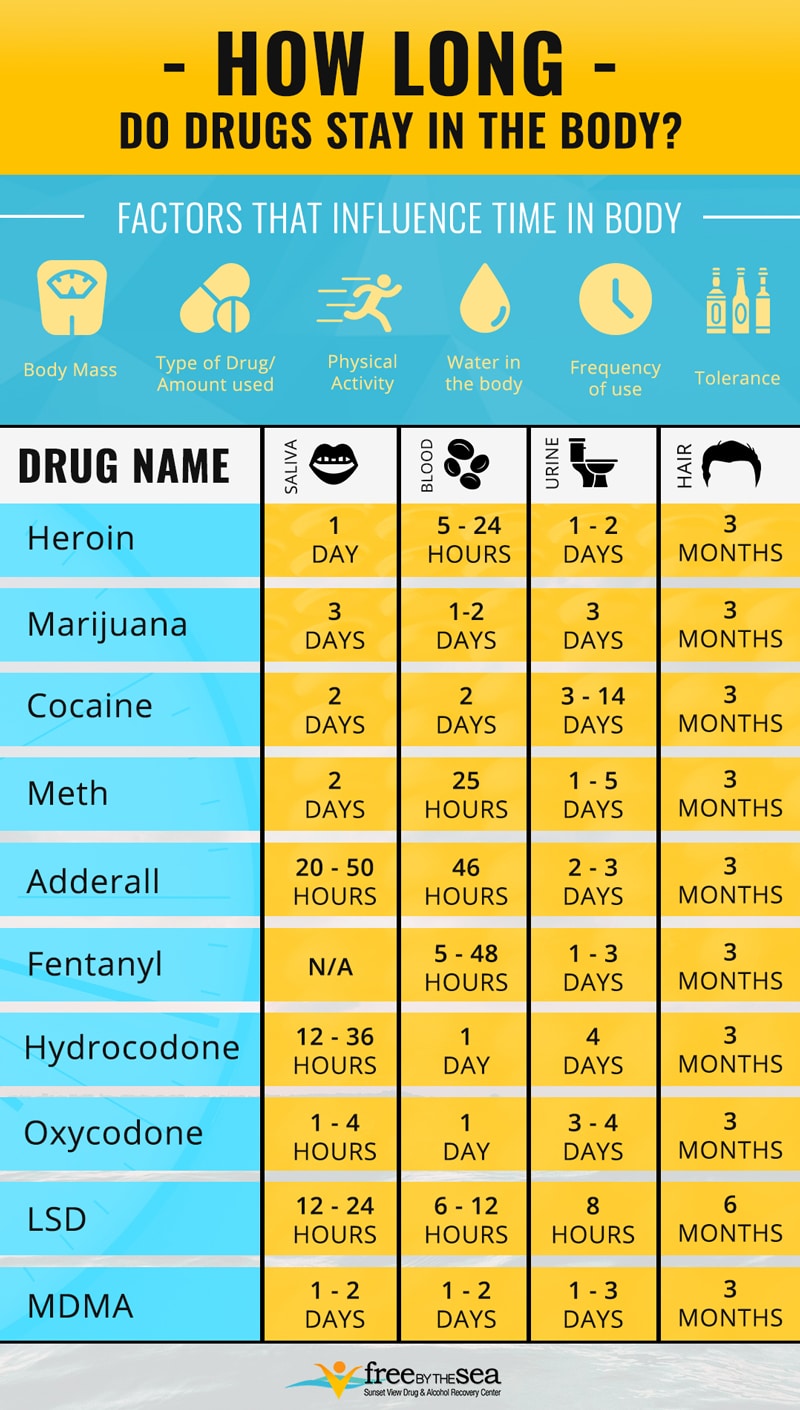
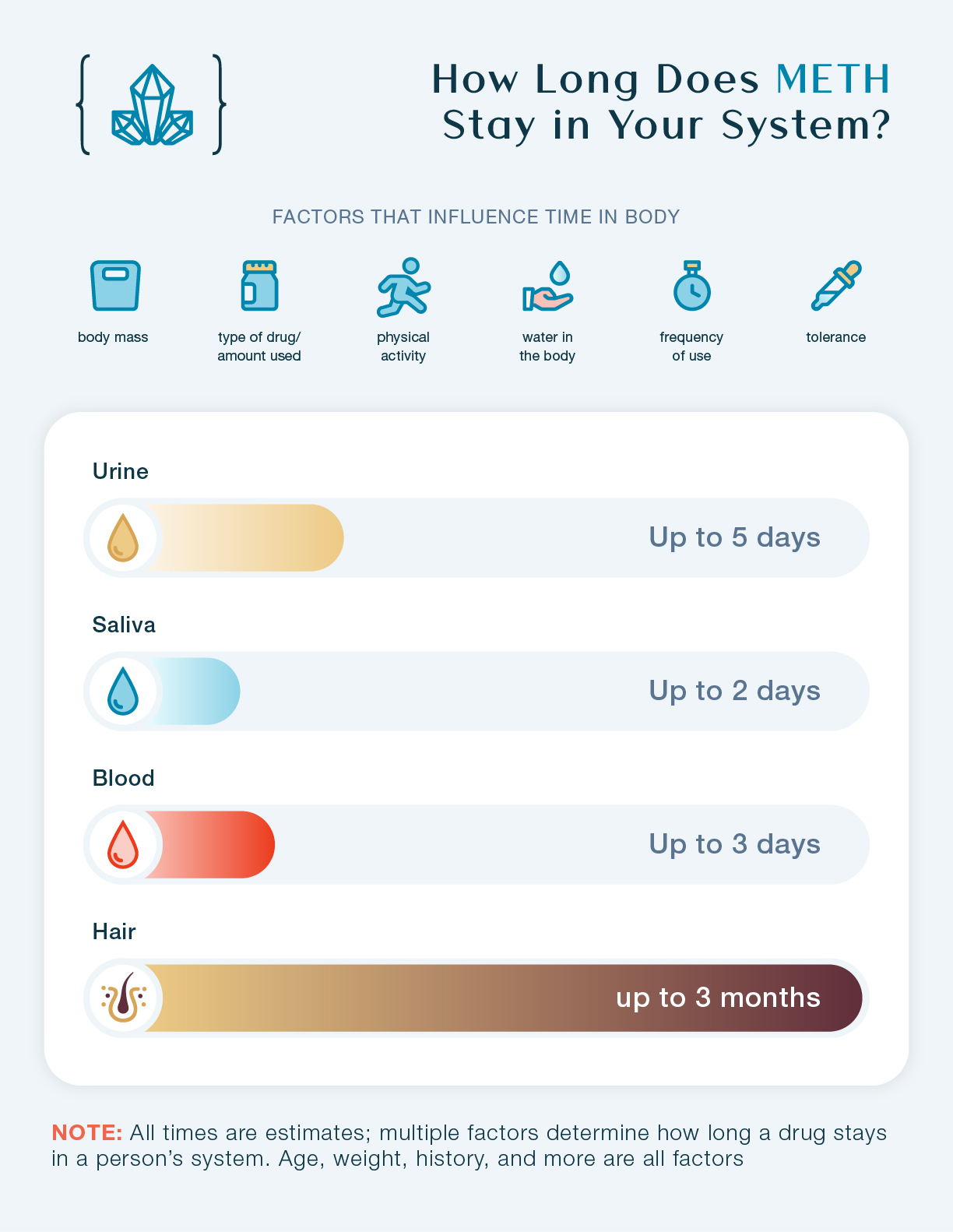
Meth detection times vary based on factors like usage frequency and metabolism. Meth can be detected in urine for up to 3-5 days after use, in blood for 1-3 days, and in hair for up to 90 days. Factors like hydration and body composition can influence detection windows.
Methamphetamine, commonly referred to as meth, is a highly addictive stimulant drug that can stay in your system for quite a while. Meth detection times refer to how long the drug can be detected in your body after use. Meth can be detected through various drug tests, including urine, blood, saliva, and hair follicle tests. The detection times for each test can differ depending on various factors. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand the factors that influence meth retention in the body and the importance of understanding meth metabolism.
Factors Influencing Meth Retention
Several factors can influence how long meth stays in your system, including:
- Dosage: The amount of meth you take can affect how long it stays in your system. Higher doses take longer to clear from the body.
- Frequency of use: Frequent use can cause the drug to accumulate in your system, leading to longer detection times.
- Method of use: Smoking or injecting meth leads to quicker absorption and elimination rates compared to snorting or orally ingesting it.
- Body composition: People with higher body fat content tend to retain meth longer than those with lower body fat content.
- Metabolism: People with a slower metabolism tend to retain meth longer than those with a faster metabolism.
Importance Of Understanding Meth Metabolism
Meth metabolism refers to how the body breaks down and eliminates the drug. Understanding meth metabolism is essential in determining meth detection times. Meth is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily through the urine. However, the drug can also be excreted through the sweat, feces, and hair. Moreover, understanding meth metabolism can help users determine how long to wait before taking a drug test. For example, if you’re a frequent user, it may take longer for meth to clear from your system than occasional users. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand how your body metabolizes the drug to avoid failing a drug test. In conclusion, meth detection times can differ depending on various factors such as dosage, frequency of use, method of use, body composition, and metabolism. Understanding these factors and how they influence meth retention in the body is crucial in determining how long the drug stays in your system. Additionally, understanding meth metabolism can help users avoid failing a drug test by determining how long to wait before taking one.
Chemical Properties Of Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine’s chemical properties determine its duration in the system. Meth can stay detectable in urine for up to 3-5 days, but in blood or saliva, it’s usually detectable for 1-3 days. Hair follicle tests can trace meth use for up to 90 days.
Meth Half-life
Methamphetamine, commonly known as meth, is a potent stimulant that affects the central nervous system. Understanding the chemical properties of methamphetamine can provide insights into how long it stays in your system. One important factor to consider is the half-life of meth.
In pharmacology, the half-life refers to the time it takes for half of a substance to be eliminated from the body. For methamphetamine, the half-life varies depending on several factors, including the individual’s metabolism, dosage, and frequency of use.
On average, the half-life of methamphetamine ranges from 10 to 12 hours. This means that after 10 to 12 hours, half of the methamphetamine ingested will be eliminated from the body. However, it’s important to note that traces of the drug can still be detected in various bodily fluids and tissues even after the half-life has passed.
Metabolic Pathways
When methamphetamine enters the body, it undergoes various metabolic pathways that contribute to its elimination. The primary metabolic pathway for methamphetamine involves hepatic metabolism, which occurs in the liver.
In the liver, methamphetamine is metabolized by enzymes, primarily the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. This system plays a crucial role in breaking down the drug into metabolites that can be eliminated from the body.
One of the major metabolites of methamphetamine is amphetamine, which also possesses stimulant effects. The metabolism of methamphetamine into amphetamine occurs through a process called N-demethylation.
After being metabolized, both methamphetamine and amphetamine undergo further breakdown and elimination through renal excretion. This means that they are excreted through urine, contributing to the detection of the drug in drug tests.
It’s important to note that factors such as pH levels, hydration, and overall health can influence the speed at which methamphetamine and its metabolites are eliminated from the body.
Meth Detection Methods
When it comes to detecting methamphetamine (meth) in the body, there are several methods that can be used to determine its presence. These methods include urine testing, blood analysis, hair follicle examination, and saliva swabs. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, providing different windows of detection for methamphetamine use.
Urine Testing
Urine testing is one of the most common methods used to detect methamphetamine in the body. It involves collecting a urine sample from the individual and analyzing it for the presence of methamphetamine and its metabolites. This method is preferred due to its non-invasive nature and relatively low cost.
Urine testing can detect methamphetamine within 2-5 hours after use and can continue to show positive results for up to 1-4 days, depending on the frequency and amount of methamphetamine used. However, it is important to note that this method may produce false negatives if the drug has been used more than a few days prior to testing.
Blood Analysis
Blood analysis is another method that can be used to detect methamphetamine in the body. This method involves drawing a blood sample from the individual and analyzing it for the presence of methamphetamine and its metabolites. Blood analysis is considered to be more accurate than urine testing, as it can provide real-time information about recent drug use.
Methamphetamine can be detected in the blood within minutes to hours after use and can remain detectable for up to 1-3 days. However, it is important to note that blood analysis is more invasive and costly compared to urine testing, making it less commonly used for routine drug screening.
Hair Follicle Examination
Hair follicle examination is a method that can provide a longer detection window for methamphetamine use. This method involves collecting a small sample of hair from the individual and analyzing it for the presence of methamphetamine and its metabolites. Hair follicle examination is often used when a longer history of drug use needs to be determined.
Methamphetamine can be detected in the hair follicles within 5-7 days after use and can continue to be detected for up to 90 days or even longer, depending on the length of the hair sample. This method is highly accurate and difficult to tamper with, making it a preferred option for forensic purposes.
Saliva Swabs
Saliva swabs, also known as oral fluid testing, are a relatively newer method for detecting methamphetamine in the body. This method involves collecting a sample of saliva from the individual and analyzing it for the presence of methamphetamine and its metabolites. Saliva swabs are non-invasive and can provide quick results.
Methamphetamine can be detected in saliva within minutes to hours after use and can continue to be detectable for up to 1-3 days. Saliva swabs are gaining popularity in certain settings such as roadside drug testing due to their ease of use and shorter detection window compared to urine and hair follicle testing.
Influence Of Dosage And Frequency
When it comes to testing for methamphetamine in the system, two key factors that can significantly impact the detection time are the dosage consumed and the frequency of use. Understanding how these factors influence the duration of meth detection can be crucial for individuals undergoing drug testing or seeking to detoxify their bodies.
Impact Of Dosage On Detection Time
The dosage of methamphetamine consumed plays a vital role in determining how long the drug can be detected in the system. Higher doses of meth can stay in the body for a longer period compared to lower doses. This is because the body takes time to metabolize and eliminate the drug.
For instance, a single-use of a low dosage of meth may be detectable in urine for around 2-3 days, while a high dosage can be detected for up to 5-7 days. The detection time can vary based on individual factors such as metabolism, body mass, and overall health.
In addition to urine, methamphetamine can also be detected in other bodily fluids such as blood, saliva, and hair. Higher doses tend to extend the detection window in these fluids as well. For example, while meth can typically be detected in blood for 1-3 days after low dosage use, it can be detected for up to 5-7 days after high dosage use.
Frequency Of Use And Test Sensitivity
The frequency of methamphetamine use is another crucial factor that affects the detection time. Regular users may have a longer detection window compared to occasional users due to the accumulation of the drug in their system.
Drug tests for meth can vary in their sensitivity, with some tests capable of detecting even trace amounts of the drug. The more sensitive the test, the longer the detection window becomes, especially for frequent users. These tests can detect methamphetamine in urine for up to 7 days or more, depending on the frequency and amount of usage.
It’s important to note that the detection times mentioned here are approximate estimates and can vary based on individual factors. Factors such as age, overall health, and metabolism can influence the rate at which methamphetamine is processed and eliminated from the body.
In conclusion, both the dosage consumed and the frequency of methamphetamine use can significantly impact how long the drug stays in the system. Higher doses and frequent use tend to extend the detection window, making it crucial for individuals to be aware of these factors when undergoing drug testing or seeking detoxification.
Individual Factors Affecting Meth Clearance
Individual factors can significantly impact how long meth stays in a person’s system. Factors such as metabolism, age, health, and lifestyle choices can influence the clearance of meth from the body. Understanding these individual factors is crucial for gaining insight into the duration of meth detection in the system.
Role Of Metabolism
Metabolism plays a pivotal role in determining how long methamphetamine stays in the system. High metabolic rates can lead to quicker clearance of meth, while slower metabolism may prolong its presence in the body.
Age And Health Considerations
Age and overall health status can also affect the duration of meth detection in the system. Younger individuals and those in good health tend to metabolize meth more efficiently, leading to faster clearance. Conversely, older individuals or those with health conditions may experience a slower clearance rate.
Lifestyle And Hydration
Lifestyle choices, such as diet and physical activity, can impact meth metabolism. Adequate hydration can support the body’s natural detoxification processes, potentially expediting meth clearance.
Credit: freebythesea.com
The Role Of Detoxification Processes
Natural Detox Mechanisms
Our bodies have natural detoxification mechanisms that work to eliminate methamphetamine and its metabolites from our system. The liver plays a key role in breaking down and processing meth, while the kidneys help to excrete the resulting byproducts. Additionally, sweating and breathing also contribute to the elimination of meth from the body.
Detox Products And Their Efficacy
Some individuals may seek out detox products to help expedite the removal of meth from their system. These products often claim to cleanse the body of toxins quickly, but their efficacy is not scientifically proven. It’s important to be cautious of the claims made by these products and to consult with a medical professional before using them.
Legal Implications Of Meth Testing
Meth can stay in your system for 2-3 days, but chronic use can be detected for up to a week. Meth testing has legal implications, as it can be used in child custody cases, property disputes, and criminal investigations. It’s important to be aware of the duration of meth’s presence in the body for potential legal matters.
In workplaces, meth testing is crucial to ensure safety and productivity.
Workplace Drug Policies
Employers may conduct random drug tests to detect meth use.
Legal Proceedings And Meth Detection
Meth detection in legal cases can impact sentencing and custody decisions.

Credit: www.therecoveryvillage.com
Support And Resources For Meth Users
Methamphetamine can stay in the system for 2-4 days, but chronic use may prolong detection. It’s crucial for meth users to seek support and resources to overcome addiction and receive proper care. Understanding the duration of meth in the system is essential for recovery and treatment planning.
Addiction Treatment Programs
Support and resources for meth users are essential in overcoming addiction.
Counseling And Support Groups
Counseling and support groups offer guidance and encouragement for recovery.
Credit: www.theedgetreatment.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Meth Stay In Your System?
Meth can stay in your system for up to 3 days. However, heavy use may be detectable for up to a week. Factors such as metabolism and frequency of use can affect detection times.
Can Meth Be Detected In A Drug Test?
Yes, meth can be detected in various drug tests, including urine, blood, saliva, and hair follicle tests. The detection window varies depending on the type of test, with urine tests typically detecting meth for 1-4 days after use.
What Are The Signs Of Meth Use?
Signs of meth use include increased energy, decreased appetite, rapid weight loss, dilated pupils, and erratic behavior. Long-term use can lead to severe dental problems, skin sores, and mood disturbances.
How Does Meth Affect The Body?
Meth affects the body by increasing dopamine levels, leading to a surge of energy and euphoria. However, it also causes increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and can lead to severe dental and skin issues over time.
Conclusion
Understanding how long meth stays in your system is crucial for various reasons. By being informed about detection times, you can make better decisions regarding your health and well-being. Remember to seek professional help if you or someone you know is struggling with methamphetamine use.
Stay informed and stay safe.



