How Many Electrons Does Oxygen Have? Unlock the Mystery!

Oxygen has 8 electrons. It is a chemical element with atomic number 8.
Oxygen, a vital element in the periodic table, plays a crucial role in various biological and chemical processes. From sustaining life through respiration to its presence in water molecules, oxygen is fundamental to our existence. Its electron configuration allows it to form bonds with other elements, creating compounds that are essential for life.
Understanding the electron count of oxygen is key to comprehending its reactivity and significance in the natural world. Let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of oxygen and explore its role in our everyday lives.
Credit: socratic.org
The Elemental Basics
Oxygen, a vital element, contains 8 electrons in its atomic structure, defining its chemical properties and reactivity. Understanding the electron configuration of oxygen is fundamental in grasping its role in various chemical reactions and biological processes.
Atomic Structure Primer
Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and they are composed of three primary subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in energy levels or shells. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines the element it represents.
Oxygen In The Periodic Table
Oxygen is a chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen has six valence electrons, which are located in the second energy level or shell. These electrons participate in chemical bonding, and they can be shared with other atoms to form chemical compounds. Oxygen is essential for life as it is a component of water and is involved in respiration. In conclusion, understanding the atomic structure of oxygen and its position on the periodic table is crucial in understanding its chemical properties and its role in our daily lives.
Electrons And Their Orbits
Electron Shells Explained
The electrons in an atom are arranged in shells or energy levels, each with a specific capacity. The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons, while the second and third shells can hold up to 8 electrons each. The arrangement of electrons in these shells determines the chemical properties of the element.
Quantum Mechanics At A Glance
Quantum mechanics describes the behavior of electrons within an atom. It explains how electrons occupy specific energy levels, also known as orbitals, within the electron shells. These orbitals are represented by various shapes and orientations and are essential in understanding the distribution of electrons in an atom.
The Oxygen Atom
Oxygen, a vital element, has eight electrons in its atomic structure. These electrons are crucial for its reactivity and bonding capabilities.
Protons
The oxygen atom, with the atomic number 8, is composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are subatomic particles that carry a positive charge. In the case of oxygen, it contains 8 protons, which determines its atomic number. Protons play a crucial role in defining an element’s identity and chemical properties.
Neutrons
Neutrons, on the other hand, are subatomic particles that have no charge. They reside in the nucleus of an atom alongside protons. While protons are responsible for the positive charge, neutrons help stabilize the nucleus. In the case of oxygen, it typically contains 8 neutrons, but there can be variations resulting in different isotopes of oxygen.
Electrons
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. They are crucial in determining an atom’s reactivity and its ability to form chemical bonds. Oxygen atoms typically have 8 electrons, equal to the number of protons. These electrons occupy different energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
Atomic Number Significance
The atomic number of an element, such as oxygen, holds significant importance. It represents the number of protons present in the nucleus, which in turn determines the element’s identity. For oxygen, the atomic number of 8 signifies that it belongs to the oxygen family and possesses unique chemical properties associated with this element. Understanding the composition of an oxygen atom, including its protons, neutrons, and electrons, allows us to comprehend its behavior and interactions with other elements. This knowledge is essential in various scientific fields and helps us appreciate the complexities of the world at the atomic level.
Unveiling Oxygen’s Electrons
Welcome to the intriguing world of oxygen’s electrons. Let’s delve into the fundamental aspects of how many electrons oxygen possesses and their roles within the atom.
Electron Count Revealed
Oxygen, with an atomic number of 8, contains 8 electrons distributed among its energy levels. These electrons play a crucial role in the chemical behavior of oxygen, influencing its reactivity and bond-forming tendencies.
Energy Levels And Valence Electrons
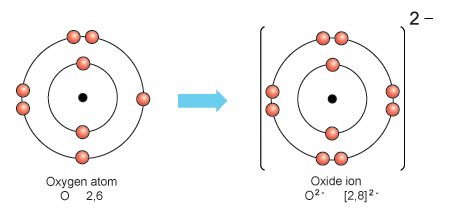
Oxygen’s electrons are organized into energy levels, with 2 electrons in the first level and 6 in the second. The outermost energy level, known as the valence shell, contains 6 electrons, which are the valence electrons. These valence electrons determine the chemical properties of oxygen, making it a vital element in various compounds and biological processes.
Chemical Bonding And Oxygen
Oxygen is a vital element in chemical reactions and plays a crucial role in the formation of compounds. Understanding the chemical bonding of oxygen is essential in comprehending its behavior and properties in various substances.
Oxygen’s Role In Compounds
Oxygen has six electrons in its outer shell, making it highly reactive and prone to forming chemical bonds with other elements. It readily forms compounds through various bonding mechanisms, such as ionic and covalent bonding.
Covalent Bonding In Action
Covalent bonding is particularly significant for oxygen, as it often forms stable covalent compounds by sharing electrons with other atoms. This type of bonding occurs when two or more atoms share electrons to achieve a more stable electron configuration.
Oxygen commonly forms covalent bonds with elements like carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen, resulting in the creation of diverse compounds. For example, in the water molecule (H2O), oxygen forms covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms, resulting in a stable and familiar substance.
Furthermore, oxygen’s ability to form multiple covalent bonds allows it to participate in complex organic molecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, which are essential for life processes.
In summary, understanding the chemical bonding of oxygen is crucial in comprehending its role in compounds. Oxygen’s highly reactive nature and its ability to form covalent bonds with various elements make it a key player in the formation of diverse substances.
Oxygen’s Electron Configuration
Oxygen’s electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in its atomic orbitals. Understanding this configuration is crucial for comprehending the chemical behavior of oxygen and its interactions with other elements. Let’s delve into the writing of electron configurations and the significance of orbital diagrams in deciphering the electron arrangement of oxygen.
Writing Electron Configurations
When writing electron configurations, it’s essential to follow the aufbau principle, which dictates that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. For oxygen, the electron configuration is written as 1s2 2s2 2p4. This signifies the distribution of its 8 electrons among the atomic orbitals.
Understanding Orbital Diagrams
Orbital diagrams visually represent the electron configuration of an element. In the case of oxygen, the orbital diagram displays two electrons in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital, and four in the 2p orbitals. This depiction aids in comprehending the spatial distribution of electrons within the atom.
Oxygen In Action
Oxygen plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and biological processes. Let’s explore how oxygen is involved in different scenarios.
Oxygen In Organic Molecules
Oxygen forms bonds with other elements to create organic compounds.
Oxygen In Oxidation And Reduction
Oxygen participates in both oxidation and reduction reactions.
Beyond The Basics
Oxygen, a vital element in our atmosphere, has 8 electrons in its atomic structure. Let’s delve deeper into the complexities of oxygen electrons.
Isotopes Of Oxygen
Isotopes of oxygen include O-16, O-17, and O-18 with varying numbers of neutrons.
Practical Applications Of Oxygen Electrons
- Oxygen electron configuration aids in understanding chemical bonding.
- Medical diagnostics utilize oxygen isotopes for imaging techniques.
- Isotopic analysis of oxygen aids in environmental research.
Credit: www.quora.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Electrons Does Oxygen Have?
Oxygen has 8 electrons. It belongs to the atomic number 8 in the periodic table, indicating the number of protons and electrons present in its nucleus. Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells.
Oxygen’s electron configuration is 2-6, with 2 electrons in the innermost shell and 6 in the outer shell.
Conclusion
Oxygen has eight electrons, two in its first energy level and six in its second energy level. These electrons are arranged in such a way that oxygen can form strong bonds with other elements, making it an essential component of many compounds.
Understanding the electron configuration of oxygen is important in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. By knowing the number and arrangement of electrons in oxygen, we can better understand its behavior and properties.



